Vue
父传子
props
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
<div id="root">
<h2>{{msg}}</h2>
<Son1 v-bind:age="18"></Son1>
</div>
<template id="son1">
<div>
<h3>{{msg}}</h3>
<p>{{age}}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
const Son1 = {
template: "#son1",
props:['age',],
data(){
return {
msg:"son"
}
}
}
var vm = new Vue({
el:"#root",
data:{
msg:"father"
},
components:{
Son1
}
})
</script>
|
子传父
$emit自定义事件
- 子组件给父组件发送自定义事件
- 父组件在子组件标签上监听自定义事件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
|
<div id="root">
<h2>{{msg}}</h2>
<Son1 @savemsgfromson="save"></Son1>
</div>
<template id="son1">
<div>
<button @click="sendEventToFather(toFather)">{{msg}}</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
const Son1 = {
template: "#son1",
data(){
return {
msg:"son",
toFather:"少抽点烟"
}
},
methods:{
sendEventToFather(message){
this.$emit('savemsgfromson',message)
}
}
}
var vm = new Vue({
el:"#root",
data:{
msg:"father"
},
components:{
Son1
},
methods:{
save(message){
console.log(message)
}
}
})
</script>
|
任何关系组件传值(EventBus和vuex)
EventBus
- EventBus称之为中央事件总线
- 通过一个空的Vue实例作为中央事件总线
- $emit自定义事件用来发送数据
- $on触发自定义事件来接收数据
- $off销毁自定义事件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
|
<div id="root">
<Son1></Son1>
<Son2></Son2>
<hr/>
<button @click="deb">销毁事件</button>
</div>
<template id="son1">
<div>
<h3>{{msg}}</h3>
<button @click="toson2">toSon2</button>
</div>
</template>
<template id="son2">
<div>
<h3>{{msg}}</h3>
</div>
</template>
<script>
const eventBus = new Vue()
const Son1 = {
template: "#son1",
data(){
return {
msg:"son1"
}
},
methods:{
toson2(){
eventBus.$emit('sendtoson2','弟弟')
}
}
}
const Son2 = {
template: "#son2",
data(){
return {
msg:"son2"
}
},
mounted(){
eventBus.$on('sendtoson2',msg=>{
console.log(msg)
})
}
}
var vm = new Vue({
el:"#root",
components:{
Son1,Son2
},
methods:{
deb(){
eventBus.$off('sendtoson2')
console.log('销毁事件')
}
}
})
</script>
|
vuex
链接
React
父传子
使用props进行父传子
父组件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| >import React from "react";
>import Item from "./Components/Item";
>class App extends React.Component {
render() {
return <Item name="林则徐" next="壁立千仞无欲则刚"></Item>;
}
>}
>export default App;
|
子组件(函数)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| >import React from "react";
>const Item = (props) => {
return (
<div>
海纳百川有容乃大,{props.next}。 -- {props.name}
</div>
);
>};
>export default Item;
|
子组件(类)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| >import React, { Component } from "react";
>class Item extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
海纳百川有容乃大,{this.props.next}。 -- {this.props.name}
</div>
);
}
>}
>export default Item;
|
子传父
该传值的实现可以分为两种,思想大致如下:
- (父主动获取子的数据)父通过
ref标记子组件,随后通过子组件实例对象获取子组件的数据
- 在父组件中预埋一个修改父组件自身的方法,将该方法以
props的形式传递给子组件,子组件收到方法时去调用,并且将自己需要给父的数据以实参的形式给这个方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
|
import React, { Component, createRef } from "react";
class Father extends Component {
child = createRef();
render() {
return (
<div>
<Son ref={this.child} fun={this.SonSetMsg.bind(this)}></Son>
{/* 方法1:父主动去获取子的数据 */}
<button onClick={this.getMsgFromSon.bind(this)}>子: 还钱!爸</button>
</div>
);
}
getMsgFromSon() {
console.log(this.child.current.state.msg);
}
SonSetMsg(msg) {
console.log(msg);
}
}
class Son extends Component {
state = {
msg: "后来学会了做空,股票涨的时候也会赔钱",
};
render() {
return (
<div>
<div>子组件</div>
<button onClick={this.setMsg.bind(this)}>子把数据放篮子里</button>
</div>
);
}
setMsg() {
this.props.fun(this.state.msg);
}
}
export default Father;
|
跨组件传值
网址:https://zh-hans.reactjs.org/docs/context.html
在react没有类似vue中的事件总线来解决这个问题。在实际的项目中,当需要组件间跨级访问信息时,如果还使用组件层层传递props,此时代码显得不那么优雅,甚至有些冗余。在react中,我们还可以使用context来实现跨级父子组件间的通信。
1
2
3
4
5
6
| import React, { Component, createContext } from "react"
const {
Provider,
Consumer
} = createContext()
|
提示:在React的context中,数据被看成了商品,发布数据的组件会用provider身份(卖方),接收数据的组件使用consumer身份(卖方)。
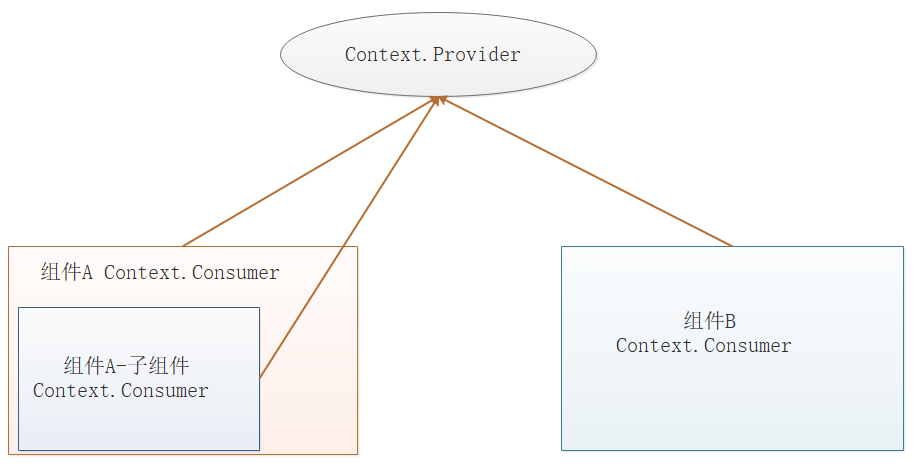
当React渲染一个订阅了这个Context对象的组件,这个组件会从组件树中离自身最近的那个匹配的Provider中读取到当前的context值。
1
2
3
4
5
|
import { createContext } from "react"
export default createContext()
|
在App.jsx组件中发布消息,这样所有的组件都可以消费它的消息。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| import React, { Component } from "react";
import Cmp1 from "./Components/Cmp1";
import Cmp2 from "./Components/Cmp2";
import ContextObj from "./Context/index";
let { Provider } = context;
class App extends Component {
state = {
count: 12345,
};
render() {
return (
<div>
<Provider value={this.state.count}>
<Cmp6></Cmp6>
<Cmp7></Cmp7>
</Provider>
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;
|
在子组件中通过Api完成消费动作,从而实现消息通信。消费的方式有2种:
方式1:通过组件消费
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| import React, { Component } from "react";
import ContextObj from "../Context/index";
let { Consumer } = ContextObj;
class Cmp1 extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<Consumer>
{(value) => {
return <div>获取到的值是:{value}</div>;
}}
</Consumer>
</div>
);
}
}
export default Cmp1;
|
方式2:通过绑定静成属性来消费
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| import React, { Component } from "react";
import ContextObj from "../Context/index";
class Cmp2 extends Component {
static contextType = ContextObj;
render() {
return <div>{this.context}</div>;
}
}
export default Cmp2;
|
任何关系组件传值
Redux

